Portable Headphone Amplifier
Circuit diagram:
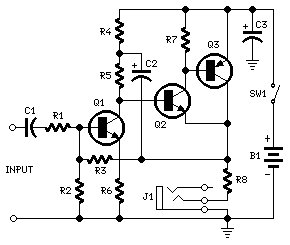
Parts
R1 = 10K 1/4W Resistor
R2 = 100K 1/4W Resistor
R3 = 68K 1/4W Resistor (see notes)
R4 = 1K5 1/4W Resistor
R5 = 3K3 1/4W Resistor
R6 = 330R 1/4W Resistor
R7 = 4K7 1/4W Resistor
R8 = 2R2 1/4W Resistor
C1 = 1ВµF 63V Polyester Capacitor
C2 = 100ВµF 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
C3 = 470ВµF 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
Q1 = BC239C 25V 100mA NPN High-gain Low-noise Transistor
Q2 = BC337 45V 800mA NPN Transistor
Q3 = BC327 45V 800mA PNP Transistor
J1 = Stereo 3mm. Jack socket
SW1 = SPST Switch
B1 = 3V Battery (two 1.5V AA or C cells in series)
Notes:
Can be directly connected to CD players, tuners and tape recorders.
Tested with several headphone models of different impedance: 32, 100, 245, 300,
600 & 2000 Ohms.
Schematic shows left channel only.
B1, SW1, J1 & C3 are common to both channels.
R3 value was calculated for headphone impedance up to 300 Ohms. Using 600 Ohms
loads or higher, change R3 value to 100K.
Technical data:
Current drain: 35mA per channel with 32 Ohms impedance headphones. Much less
with higher impedance loads
Output voltage: Above 2V peak-to-peak on all loads
Sensitivity: 90mV RMS input for 2V peak-to-peak output
Frequency response: Flat from 30Hz to 20KHz
Total harmonic distortion @ 1KHz & 10KHz: Below 0.05% on 32 to 600 Ohms load and
up to 1.5V peak-to-peak output. Below 0.1% at maximum output
Unconditionally stable on capacitive loads
Title: Portable Headphone Amplifier
electronic circuit
Source: www.redcircuits.com
Published on: 2005-02-01
Reads: 1393
Print version: ![]()
Other electronic circuits and schematics from Audio
-
Phono Preamplifier
-
Mini-box 2W Amplifier
-
Amplifier of acoustic frequencies with preamplifier
-
Two transistor audio amplifier circuit
-
Ultrasonic pest repellent
-
Bass-treble tone control circuit
-
Sound detector latch
-
Portable Microphone Preamplifier
-
Precision Audio Millivoltmeter
-
50 Watt Amplifier
